Reduced blood flow
The relationship between the mother going to sleep lying on her back and stillbirth is biologically plausible. A supine position in late pregnancy is associated with reduced blood flow to the womb. Hence, women in labour and women having a caesarean section are routinely tilted onto their side to improve blood supply to the baby.
Recent research carried out at the University of Auckland has provided sophisticated evidence about how the mothers’ position influences blood flow. Results obtained using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) demonstrate the major vessel in the mother’s abdomen, the inferior vena cava, being compressed by the pregnant womb when she is lying on her back. This reduces flow through this vessel by 80%.
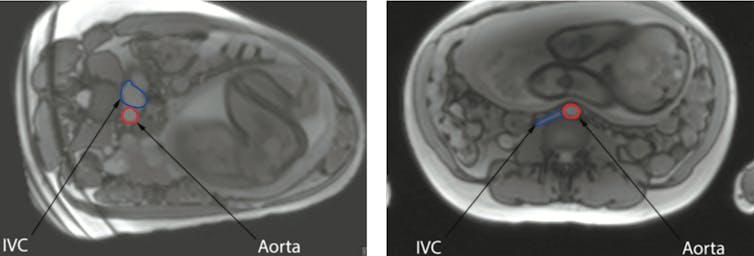
Although the mother’s circulation responds by increasing the flow through other veins, this does not fully compensate. The mother’s aorta, the main artery which carries oxygen-rich blood from her heart, is also partly compressed when the mother lies on her back. This decreases blood flow to the pregnant uterus, placenta and baby.
We speculate that while healthy unborn babies can compensate for the reduced blood supply, babies that are unwell or vulnerable for some other reason may not cope. For example, our mega study showed that the risk of stillbirth after 28 weeks of pregnancy is increased approximately 16 times if a mother goes to sleep lying on her back and also is pregnant with a very small baby.
What to do
New Zealand research has shown that pregnant women can change their sleeping position. In a recent survey conducted in pregnant women from south Auckland, a community that has a high rate of stillbirth, more than 80% of women surveyed stated that they could change the position they went to sleep in with little difficulty if it was best for their baby.
Our advice to pregnant women from 28 weeks of pregnancy is to settle to sleep on their side to reduce the risk of stillbirth, and to start every sleep, including day-time naps, on the side. It does not matter which side. It is common to wake up on the back, but we recommend that if this happens, women should simply roll back on to either side.
By Lesley McCowan, Professor, Obstetrics & Gynecology, University of Auckland and Robin Cronin, Midwife researcher, University of Auckland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.










